For drummers, mastering how to read drum notation is crucial to playing complex rhythms and grooves with precision.
This guide will help you grasp the essentials, from understanding drum sheet music to recognizing notation symbols and interpreting drum scores.
To understand sheet music you will have to learn to read the staff, key signatures, clefs, and note values guide you in playing the music correctly, with rhythms dictated by the arrangement of notes within measures.
Understanding Drum Sheet Music
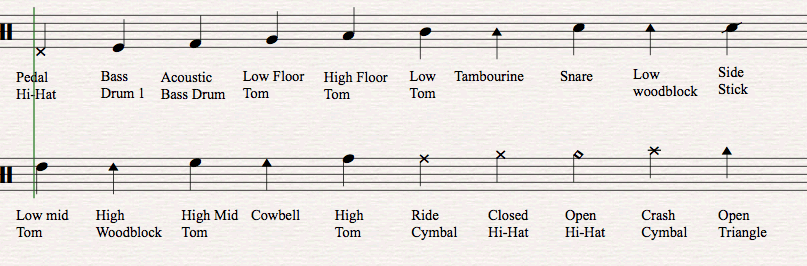
Drum sheet music uses a staff with five lines and four spaces, much like other musical instruments.
Each drum set component is placed on a specific line or space.
The bass drum is usually at the bottom, reflecting its lower pitch, while cymbals sit at the top due to their higher pitch.
Symbols Explained
Drum Notation Symbols
- Notes: Drums are indicated with dots, and cymbals often with an “x.” Stems show the rhythm.
- Rests: Signify silence or when not to play a drum.
- Time Signature: Displays the number of beats per measure and the note value of each beat, like 4/4.
Common Symbols
- Bass Drum: Notated in the bottom space of the staff.
- Snare Drum: Typically found in the middle of the staff.
- Cymbals: Marked with an “x” and usually at the top of the staff.
Understanding Drum Scores
- Time Signature: Always at the sheet’s beginning, indicating any changes.
- Note Lengths: Includes quarter notes, half notes, whole notes, and smaller fractions like eighth and sixteenth notes.
- Tuplets: Enable playing more notes in a shorter time frame, such as triplets.
Reading Drum Scores Effectively
Mastering drum notation is an essential skill and it will influence everything you will do in the future.
It is crucial to learn to read the drum scores and it will open a lot of new possibilities.
While it may seem daunting at first, a structured approach to reading drum scores can make the process much easier and more intuitive.
Counting beats and rhythm
Understanding rhythm is the cornerstone of reading drum notation.
Effective beat counting is essential because drummers are in charge of keeping a piece’s tempo and groove.
Here are some tips for enhancing your understanding of rhythm:
- Learn Common Time Signatures: A piece’s rhythmic structure is determined by its time signature. The most popular time signatures are 4/4, In3/4 (waltz time), and 7/8 (odd time signature), which present various rhythmic difficulties.
- Develop Internal Timing: Consistent timing is reinforced and accuracy is increased when practicing with a metronome or drum machine.
- Divide Notes: To better comprehend intricate patterns, divide rhythms into smaller note values, such as eighth and sixteenth notes.
- Counting Loud: Try tapping out the rhythm on your lap or counting aloud before playing it on the drum kit when you are first learning a drum score. Prior to converting it into actual movement, this helps to reinforce timing.
Understand Crucial Notation Markings
It’s crucial to focus on particular notations that specify how and when to play particular drum set elements when reading drum scores:
Repeat Signs (𝄆𝄇): These symbols help drummers save time and maintain score organization by telling them to repeat a particular musical passage.
Accents ( > ): Accents are placed above or below a note to suggest that a certain stroke should be played louder for emphasis.
Ghost Notes (): Often used on the snare drum, these lightly played strokes add subtle variations to the groove and are frequently used in jazz and funk drumming.
Drags and Flams: These grace notes denote embellishments that accentuate rudiments and fills.
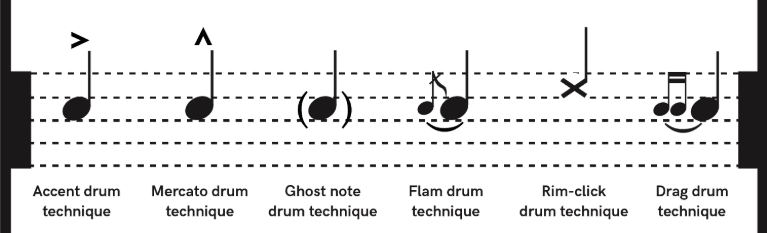
Gaining an understanding of these markings will improve your ability to interpret scores and give your playing more melody.
Essential Tips for Beginners
If you’re just starting to read drum notation these tips will definitely help you:
Familiarise Yourself with the Drum Kit Layout
In drum notation each drum and cymbal has a specific position on the staff.
Knowing where each component (e.g. snare, bass drum, hi-hat) is notated will make it much easier to read.
Start Simple
Begin with basic 4/4 beats, using quarter and eighth notes then move on to more complicated rhythms like syncopation and odd time signatures.
Slow Down and Build Accuracy First
Play slow before you speed up. Accuracy is more important than playing fast when learning notation. And speed will come once you are accurate 🙂
Practice Daily and Be Consistent
Like learning a new language, reading drum notation requires daily practice. Consider joining Drumeo or any other online platform. Even 10-15 minutes a day can lead to steady progress over time.
Use Drum Tabs as a Supplementary Tool
While traditional notation is the ultimate goal, drum tabs can be a simplified way to learn beats and fills especially for beginners.
Play Along with Songs
Try reading drum scores while listening to music.
Following along with sheet music while hearing the rhythm in context will help recognition and execution.
Get Feedback from Other Drummers
Whether it’s an instructor, a fellow drummer or an online community, getting feedback on your notation reading will be invaluable for improvement.
Mastering drum notation comes with a learning curve, and while it’s challenging to pinpoint exactly how long it will take, perseverance is key.
For a clearer idea of the timeline and helpful tips on the learning process, consider reading our article on how long does it take to learn drums effectively.
Conclusion
Learning to read drum notation unlocks a world of musical possibilities for drummers.
By understanding drum sheet music, recognizing notation symbols, and interpreting drum scores, you can enhance your drumming skills and explore a wide range of musical styles.



